C 的指针变量提供了间接方式访问程序内存。通过了解如何使用指针变量,程序员可以编写功能强大且高效的 C 程序。例如,通过指针变量,C 程序员可以:
- 在调用函数栈帧中修改参数值
- 在运行时根据需要动态分配(和释放)程序内存
- 有效地将大型数据结构传递给函数
- 创建链接的动态数据结构
- 以不同的方式解释程序存储器的字节
在本节中,我们介绍 C 指针变量的语法和语义,并介绍如何在 C 程序中使用它们的常见示例。
2.2.1. Pointer Variables
指针变量可以存储特定类型值的内存位置的地址。例如,指针变量可以存储int类型的地址, 该地址上存储数值 12。指针变量 指向(引用)值。指针提供了 间接方式 来访问内存中的值。图 1 展示了指针变量在内存中的样子:
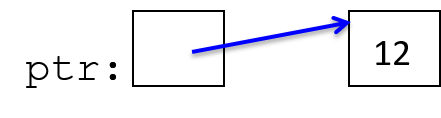 图 1. 指针变量存储内存中某个位置的地址。这里,指针存储保存数字 12 的整型变量的地址。
图 1. 指针变量存储内存中某个位置的地址。这里,指针存储保存数字 12 的整型变量的地址。
通过指针变量 ,可以间接访问它所指向的内存位置中存储的ptr值 (12)。 C 程序最常将指针变量用于:
- “Pass by pointer(传指针)” 参数,用于编写可以通过指针参数修改其参数值的函数
- 动态内存分配,用于编写在程序运行时分配(和释放)空间的程序。动态内存通常用于动态分配数组。当程序员在编译时不知道数据结构的大小(例如,数组大小取决于运行时的用户输入)时,它非常有用。它还允许在程序运行时调整数据结构的大小。
指针变量使用规则
使用指针变量的规则与常规变量类似,只不过需要考虑两种类型:指针变量的类型以及指针变量指向的内存地址中存储的类型。
-
首先,使用以下方法声明一个指针变量
type_name *var_name:int *ptr; // stores the memory address of an int (ptr "points to" an int) char *cptr; // stores the memory address of a char (cptr "points to" a char)
pointer types
请注意,虽然ptr和cptr都是指针,但它们指的是不同的类型:
ptr的类型是_“指向 int 的指针”_ (int *)。它可以指向存储值的内存位置int。cptr的类型是_“指向 char 的指针”_ (char *)。它可以指向存储值的内存位置char。
-
接下来,初始化指针变量(使其指向某个东西)。指针变量 存储地址值。应初始化指针来存储其类型与指针变量指向的类型相匹配的内存位置的地址。初始化指针的一种方法是对变量使用地址运算符(
&) 来获取变量的地址值:int x; char ch; ptr = &x; // ptr gets the address of x, pointer "points to" x cptr = &ch; // cptr gets the address of ch, pointer "points to" ch
图 2. 程序可以通过将合适的类型的现存变量地址分配给指针来初始化该指针。以下是由于类型不匹配导致的无效指针初始化的示例:
cptr = &x; // ERROR: cptr can hold a char memory location // (&x is the address of an int)尽管 C 编译器可能允许这种类型的赋值(带有有关不兼容类型的警告),但访问和修改
xthrough的行为cptr可能不会按照程序员的预期运行。相反,程序员应该使用int *变量来指向int存储位置。所有指针变量还可以分配一个特殊值NULL,它表示无效地址。虽然空指针(其值为
NULL)不应用于访问内存,但该值NULL对于测试指针变量以查看它是否指向有效的内存地址很有用。也就是说,C 程序员通常会NULL在尝试访问指针所指向的内存位置之前检查指针,以确保其值不存在。将指针设置为NULL:ptr = NULL; cptr = NULL; 图 3. 任何指针都可以被赋予特殊值 NULL,这表明它不引用任何特定地址。空指针永远不应该被取消引用。
图 3. 任何指针都可以被赋予特殊值 NULL,这表明它不引用任何特定地址。空指针永远不应该被取消引用。 -
最后,使用指针变量:解引用运算符(
*) 跟随指针变量到它指向的内存位置并访问该位置的值:/* Assuming an integer named x has already been declared, this code sets the value of x to 8. */ ptr = &x; /* initialize ptr to the address of x (ptr points to variable x) */ *ptr = 8; /* the memory location ptr points to is assigned 8 */ 图 4. 取消引用指针可访问指针所引用的值。
图 4. 取消引用指针可访问指针所引用的值。
指针示例
下面是使用两个指针变量的 C 代码示例:
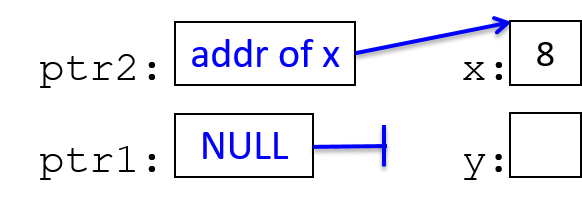
int *ptr1, *ptr2, x, y;
x = 8;
ptr2 = &x; // ptr2 is assigned the address of x
ptr1 = NULL;
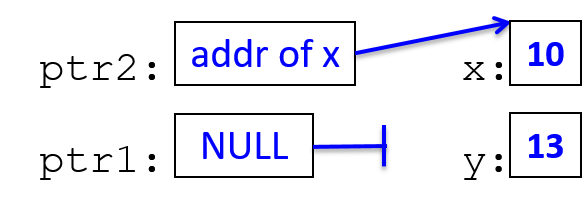
*ptr2 = 10; // the memory location ptr2 points to is assigned 10
y = *ptr2 + 3; // y is assigned what ptr2 points to plus 3
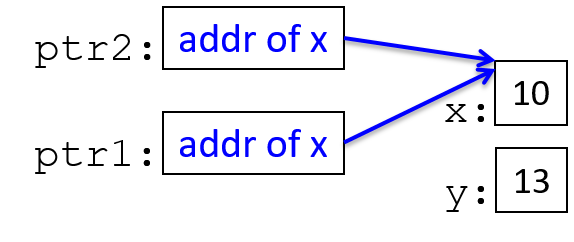
ptr1 = ptr2; // ptr1 gets the address value stored in ptr2 (both point to x)
*ptr1 = 100;
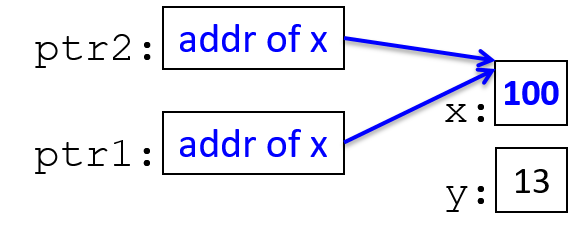
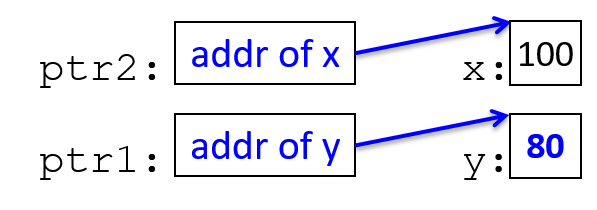
ptr1 = &y; // change ptr1's value (change what it points to)
*ptr1 = 80;
使用指针变量时,请仔细考虑相关变量的类型。绘制内存图片(如上所示)可以帮助理解指针代码正在做什么。一些常见错误涉及误用取消引用运算符 (*) 或地址运算符 (&)。例如:
ptr = 20; // ERROR?: this assigns ptr to point to address 20
ptr = &x;
*ptr = 20; // CORRECT: this assigns 20 to the memory pointed to by ptr
如果您的程序取消引用不包含有效地址的指针变量,程序将崩溃:
ptr = NULL;
*ptr = 6; // CRASH! program crashes with a segfault (a memory fault)
ptr = 20;
*ptr = 6; // CRASH! segfault (20 is not a valid address)
ptr = x;
*ptr = 6; // likely CRASH or may set some memory location with 6
// (depends on the value of x which is used as an address value)
ptr = &x; // This is probably what the programmer intended
*ptr = 6;
这些类型的错误说明了将指针变量初始化为 的原因之一 NULL;然后,程序可以在NULL取消引用指针之前测试指针的值:
if (ptr != NULL) {
*ptr = 6;
}